|
1.實(shí)驗(yàn)?zāi)康?/strong>
通過(guò)編寫(xiě)多進(jìn)程程序,使讀者熟練掌握fork()、exec()、wait()和waitpid()等函數(shù)的使用,進(jìn)一步理解在Linux中多進(jìn)程編程的步驟。
2.實(shí)驗(yàn)內(nèi)容
該實(shí)驗(yàn)有3個(gè)進(jìn)程,其中一個(gè)為父進(jìn)程,其余兩個(gè)是該父進(jìn)程創(chuàng)建的子進(jìn)程,其中一個(gè)子進(jìn)程運(yùn)行“l(fā)s -l”指令,另一個(gè)子進(jìn)程在暫停5s后異常退出。父進(jìn)程先用阻塞方式等待第一個(gè)子進(jìn)程的結(jié)束,然后用非阻塞方式等待另一個(gè)子進(jìn)程的退出,待收集到第二個(gè)子進(jìn)程結(jié)束的信息后,父進(jìn)程就返回。
3.實(shí)驗(yàn)步驟
(1)畫(huà)出該實(shí)驗(yàn)流程圖。該實(shí)驗(yàn)流程圖如圖1所示。
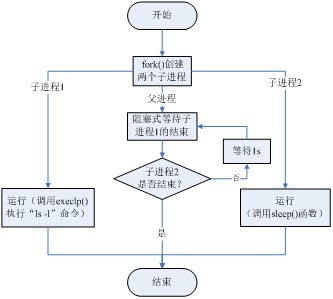
圖1 實(shí)驗(yàn)流程圖
(2)實(shí)驗(yàn)源代碼。先看一下下面的代碼,這個(gè)程序能得到我們所希望的結(jié)果嗎?它的運(yùn)行會(huì)產(chǎn)生幾個(gè)進(jìn)程?請(qǐng)讀者回憶一下fork()調(diào)用的具體過(guò)程。
/* multi_proc_wrong.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t child1, child2, child;
/* 創(chuàng)建兩個(gè)子進(jìn)程 */
child1 = fork();
child2 = fork();
/* 子進(jìn)程1的出錯(cuò)處理 */
if (child1 == -1)
{
printf("Child1 fork error\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 在子進(jìn)程1中調(diào)用execlp()函數(shù) */
else if (child1 == 0)
{
printf("In child1: execute 'ls -l'\n");
if (execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL) < 0)
{
printf("Child1 execlp error\n");
}
}
/* 子進(jìn)程2的出錯(cuò)處理 */
if (child2 == -1)
{
printf("Child2 fork error\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 在子進(jìn)程2中使其暫停5s */
else if( child2 == 0 )
{
printf("In child2: sleep for 5 seconds and then exit\n");
sleep(5);
exit(0);
}
/* 在父進(jìn)程中等待兩個(gè)子進(jìn)程的退出 */
else
{
printf("In father process:\n");
child = waitpid(child1, NULL, 0); /* 阻塞式等待 */
if (child == child1)
{
printf("Get child1 exit code\n");
}
else
{
printf("Error occured!\n");
}
do
{
child = waitpid(child2, NULL, WNOHANG);/* 非阻塞式等待 */
if (child == 0)
{
printf("The child2 process has not exited!\n");
sleep(1);
}
} while (child == 0);
if (child == child2)
{
printf("Get child2 exit code\n");
}
else
{
printf("Error occured!\n");
}
}
exit(0);
}
編譯和運(yùn)行以上代碼,并觀察其運(yùn)行結(jié)果。它的結(jié)果是我們所希望得到的嗎?
看完前面的代碼后,再觀察下面的代碼,比較一下它們之間有什么區(qū)別,看看會(huì)解決哪些問(wèn)題。
/* multi_proc.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t child1, child2, child;
/* 創(chuàng)建兩個(gè)子進(jìn)程 */
child1 = fork();
/* 子進(jìn)程1的出錯(cuò)處理 */
if (child1 == -1)
{
printf("Child1 fork error\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 在子進(jìn)程1中調(diào)用execlp()函數(shù) */
else if (child1 == 0)
{
printf("In child1: execute 'ls -l'\n");
if (execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL) < 0)
{
printf("Child1 execlp error\n");
}
}
/* 在父進(jìn)程中再創(chuàng)建進(jìn)程2,然后等待兩個(gè)子進(jìn)程的退出 */
else
{
child2 = fork();
/* 子進(jìn)程2的出錯(cuò)處理 */
if (child2 == -1)
{
printf("Child2 fork error\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 在子進(jìn)程2中使其暫停5s */
else if(child2 == 0)
{
printf("In child2: sleep for 5 seconds and then exit\n");
sleep(5);
exit(0);
}
printf("In father process:\n");
…(以下部分與前面程序的父進(jìn)程執(zhí)行部分相同)
}
exit(0);
}
(3)首先在宿主機(jī)上編譯、調(diào)試該程序:
$ gcc multi_proc.c –o multi_proc(或者使用Makefile)
(4)在確保沒(méi)有編譯錯(cuò)誤后,使用交叉編譯該程序:
$ arm-linux-gcc multi_proc.c –o multi_proc (或者使用Makefile)
(5)將生成的可執(zhí)行程序下載到目標(biāo)板上運(yùn)行。
4.實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果
在目標(biāo)板上運(yùn)行的結(jié)果如下(具體內(nèi)容與各自的系統(tǒng)有關(guān)):
$ ./multi_proc
In child1: execute 'ls -l' /* 子進(jìn)程1的顯示, 以下是“l(fā)s –l”的運(yùn)行結(jié)果 */
total 28
-rwxr-xr-x 1 david root 232 2008-07-18 04:18 Makefile
-rwxr-xr-x 1 david root 8768 2008-07-20 19:51 multi_proc
-rw-r--r-- 1 david root 1479 2008-07-20 19:51 multi_proc.c
-rw-r--r-- 1 david root 3428 2008-07-20 19:51 multi_proc.o
-rw-r--r-- 1 david root 1463 2008-07-20 18:55 multi_proc_wrong.c
In child2: sleep for 5 seconds and then exit /* 子進(jìn)程2的顯示 */
In father process: /* 以下是父進(jìn)程顯示 */
Get child1 exit code /* 表示子進(jìn)程1結(jié)束(阻塞等待) */
The child2 process has not exited! /* 等待子進(jìn)程2結(jié)束(非阻塞等待) */
The child2 process has not exited!
The child2 process has not exited!
The child2 process has not exited!
The child2 process has not exited!
Get child2 exit code /* 表示子進(jìn)程2終于結(jié)束了*/
本文選自華清遠(yuǎn)見(jiàn)嵌入式培訓(xùn)教材《從實(shí)踐中學(xué)嵌入式Linux應(yīng)用程序開(kāi)發(fā)》
熱點(diǎn)鏈接:
1、Linux下多進(jìn)程編程之exec函數(shù)語(yǔ)法及使用實(shí)例
2、Linux下多進(jìn)程編程之fork()函數(shù)語(yǔ)法
3、Linux下多進(jìn)程編程之fork()函數(shù)說(shuō)明
4、Linux守護(hù)進(jìn)程
5、wait()和waitpid()函數(shù)
更多新聞>> |

